Ship Hydrodynamics
For queries about this topic, contact Stephen Turnock.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects
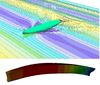
Coupled Fluid-Structure Interaction to model Three-Dimensional Dynamic Behaviour of Ships in Waves
Pandeli Temarel, Zhi-Min Chen (Investigators), Puram Lakshmynarayanana
In the present study we focus our attention on fluid-structure interactions (FSI) of flexible marine structures in waves by coupling a fluid solver using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and a structural solver using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software.
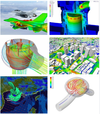
Massively-Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics
Simon Cox, Stephen Turnock, Alexander Phillips (Investigators), James Hawkes
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a numerical method for modelling fluid flows and heat transfer - and is used in many industries. It can be used to model dynamics around aircraft, ships and land vehicles; and also has uses in engine design, architecture, weather forecasting, medicine, computer-generated imagery (CGI) and much more. To harness the full power of CFD, it is necessary to utilise the full power of modern supercomputers. This project aims to improve the scalabilty of existing CFD codes so that more complex problems can be tackled efficiently.
Mixed FEM-particle method for nonlinear fluid-structure interaction problems, with applications to maritime engineering
Kamal Djidjeli (Investigator)
Simulating fluid-structure interaction problems involving large flow motions and deformations using particle methods.
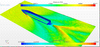
Prediction of Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Planing Hulls using CFD
Kamal Djidjeli (Investigator)
Performance prediction is an important part of vessel design. Common methods used for predicting planing hull performance include empirical equations and model tests. Model tests are usually expensive, while empirical equations are often applicable to similar hull types. In this work, CFD is used as an alternative prediction tool for high speed planing vessels.

Unsteady Aerodynamics of Wings in Extreme Conditions
Charles Badoe (Investigator), Neil Sandham, Zheng-Tong Xie
Sizing of civil aircraft is dictated by extreme loads experienced at the limits of flight envelope, for example during gust, turbulence or low speed manoeuvre. The project aims to understand the unsteady aerodynamic behaviour of wings in extreme conditions involving heaving motions near stall.
People
 Simon Cox
Simon CoxProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Neil Sandham
Neil SandhamProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Pandeli Temarel
Pandeli TemarelProfessor, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Stephen Turnock
Stephen TurnockProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Zheng-Tong Xie
Zheng-Tong XieProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Zhi-Min Chen
Zhi-Min ChenLecturer, Chemistry (FNES)
 Kamal Djidjeli
Kamal DjidjeliLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Felipe Alves Portela
Felipe Alves PortelaResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Charles Badoe
Charles BadoeResearch Fellow, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 James Hawkes
James HawkesPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Puram Lakshmynarayanana
Puram LakshmynarayananaPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Hossam Ragheb
Hossam RaghebPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stefano Spagnolo
Stefano SpagnoloPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alexander Phillips
Alexander PhillipsNone, None
 Daisuke Sasaki
Daisuke SasakiNone, None