Perl

Perl is a general-purpose programming language originally developed for text manipulation and now used for a wide range of tasks including system administration, web development, network programming, GUI development, and more. The language is intended to be practical which means easy to use, efficient and complete. It supports both procedural and object-oriented (OO) programming and has powerful built-in support for text processing (http://www.perl.org).
For queries about this topic, contact Gaia Andreoletti.
Projects
Application of RNA-Seq for gene fusion identification in blood cancers
William Tapper (Investigator), Marcin Knut
Gene fusions are often the cause of different blood cancers. As such, accurate identification of them provides information on the underlying cause of a cancer, ensuring appropriate choice of treatment. However, due to shortcomings of the currently applied methods for gene fusion identification, some of them escape undetected. We are employing RNA-Seq, a cutting-edge method for sequencing RNA, the messenger of genetic information, to investigate gene fusions.
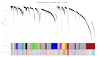
Identification of Gene-Modules Associated to a Predisposition of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Christopher Woelk (Investigator), Michael Breen
The predisposing genetic factors associated to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) are altogether unknown. Since not all trauma-survivors later develop the PTSD, it has been hypothesized that transcript differentiation prior–to-trauma exposure could be associated to the risk and resilience of PTSD. We apply a systems-level approach to investigate changes in transcript abundance (gene expression profiles) in whole blood of U.S. Marines sampled prior-to-deployment to the battlefield and followed through-out a seven month deployment to obtain disorder related outcomes.

Identifying variants in next generation sequencing data of 61 paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients
Sarah Ennis (Investigator), Gaia Andreoletti
This study aims to characterise the mutations of genes known to predispose Inflammatory bowel disease in 61 paediatric patients using next generation sequencing analysis. Our aim is to identify the relative impact of known genes in individual case presentations of disease and correlate matches with clinical manifestation.

Mathematical tools for analysis of genome function, linkage disequilibrium structure and disease gene prediction
Mahesan Niranjan, Andrew Collins, Reuben Pengelly (Investigators)
This iPhD project uses a Gaussian Bayesian Networks framework through Machine learning methods to predict which genes are involved in the development of different diseases.

Mathematical tools for analysis of genome function, linkage disequilibrium structure and disease gene prediction
Andrew Collins, Mahesan Niranjan, Reuben Pengelly (Investigators), Alejandra Vergara Lope
This iPhD project uses a Gaussian Bayesian Networks approaches framework through machine learning approach to predict which genes are involved in the development of different diseases.

Mathematical tools for analysis of genome function, linkage disequilibrium structure and disease gene prediction
Mahesan Niranjan, Andrew Collins, Reuben Pengelly (Investigators)
This PhD project uses a Monte Carlo molecular simulation processes approach to predict which genes are involved in the development of different diseases.

Sample tracking in whole-exome sequencing projects
Andrew Collins, Sarah Ennis (Investigators), Reuben Pengelly
Whole-exome sequencing is entering clinical use for genetic investigations, and it is therefore essential that robust quality control is utilised. As such we designed and validated a tool to allow for unambiguous tying of patient data to a patient, to identify, and thus prevent errors such as the switching of samples during processing.

THE NORM MATE TRANSPORTER FROM N. GONORRHEAE: INSIGHTS INTO DRUG & ION BINDING FROM ATOMISTIC MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS
Syma Khalid (Investigator), Daniel Holdbrook, Thomas Piggot, Yuk Leung
The multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) transporters extrude a wide variety of substrates out of both mammalian and bacterial cells via the electrochemical gradient of protons and cations across the membrane. Multiple atomistic simulation are performed on a MATE transporter, NorM from Neisseria gonorrheae (NorM_NG) and NorM from Vibrio cholera (NorM_VC). These simulations have allowed us to identify the nature of the drug-protein/ion-protein interactions, and secondly determine how these interactions contribute to the conformational rearrangements of the protein.
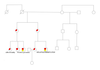
Whole exome sequencing identifies novel FLNA mutation in familial Ebstein's anomaly
Jane Gibson, Andrew Collins, Sarah Ennis (Investigators), Gaia Andreoletti
We describe the application of whole-exome sequencing in a family in which eight people in three generations presented Ebstein's anomaly.
People
 Andrew Collins
Andrew CollinsProfessor, Medicine (FM)
 Sarah Ennis
Sarah EnnisProfessor, Medicine (FM)
 Mahesan Niranjan
Mahesan NiranjanProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Robert Ewing
Robert EwingSenior Lecturer, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Reuben Pengelly
Reuben PengellySenior Lecturer, Medicine (FM)
 Jane Gibson
Jane GibsonLecturer, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Syma Khalid
Syma KhalidPrincipal Research Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Otello Roscioni
Otello RoscioniResearch Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Gaia Andreoletti
Gaia AndreolettiPostgraduate Research Student, Medicine (FM)
 Michael Breen
Michael BreenPostgraduate Research Student, Medicine (FM)
 Marcin Knut
Marcin KnutPostgraduate Research Student, Medicine (FM)
 Andrew Lawson
Andrew LawsonPostgraduate Research Student, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Yuk Leung
Yuk LeungPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Alejandra Vergara Lope
Alejandra Vergara LopePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jess Jones
Jess JonesTechnical Staff, iSolutions
 Daniel Holdbrook
Daniel HoldbrookNone, None
 Thomas Piggot
Thomas PiggotNone, None
 Daisuke Sasaki
Daisuke SasakiNone, None
 Roshan Sood
Roshan SoodNone, None
 William Tapper
William TapperNone, None
 Christopher Woelk
Christopher WoelkNone, None
 Sheng Yang
Sheng YangNone, None