Advanced modelling for two-phase reacting flow
- Started
- 1st October 2010
- Ended
- 30th September 2015
- Investigators
- Edward Richardson
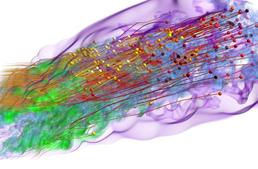
Simulation by C.S.Yoo, E.S.Richardson, R.Sankaran, and J.H. Chen. Visualisation by H. Yu and R.W. Grout. This is a visualization of a turbulent lifted Ethylene/air jet flame in an autoignitive coflow with tracer particles colored by temperature.
Engine designers want computer programs to help them invent ways to use less fuel and produce less pollution. But the computational models currently available are not adequate to predict some important effects: such as how blends of future carbon-neutral bio-fuels will change engine performance.
This research aims to provide an accurate and practical model for the injection and combustion of liquid fuel blends. High-resolution simulation data is analysed to provide fundamental information on the coupling between gasses and liquids. This information is being used to synthesise advanced models for turbulence, evaporation and combustion into a practical model framework.
The principal activities in this research are: 1) Direct Numerical Simulation of turbulent combustion, of turbulent sprays, and of multi-component droplet evaporation; 2) Development of the Large Eddy Simulation method for application to energy intensive industrial processes - gas turbine combustion in particular.
Categories
Physical Systems and Engineering simulation: CFD, Climate, Combustion, Complex fluids, Energy, Heat transfer, Turbulence
Algorithms and computational methods: Finite differences, Finite volume, Monte Carlo, Multi-physics, Multi-scale
Visualisation and data handling methods: Data Management, Surface imaging
Visualisation and data handling software: Gnuplot, HDF5, ParaView, TecPlot, VisIt, Xmgrace
Software Engineering Tools: Emacs, SVN, Trac, Vim
Programming languages and libraries: C++, Fortran, MPI, OpenMP, PETSc
Computational platforms: HECToR, HPCx, Iridis, Linux, Mac OS X
Transdisciplinary tags: HPC, Scientific Computing