Xmgrace

Grace is a free WYSIWYG 2D graph plotting tool, for Unix-like operating systems. The package name stands for "GRaphing, Advanced Computation and Exploration of data." Grace uses the X Window System and Motif for its GUI. It has been ported to VMS, OS/2, and Windows 9*/NT/2000/XP (on Cygwin). In 1996, Linux Journal described Xmgr (an early name for Grace) as one of the two most prominent graphing packages for Linux. (more from Wikipedia)
For queries about this topic, contact Hans Fangohr.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects

Ab initio simulations of chemical reactions on platinum nanoparticles
Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigator), Álvaro Ruiz-Serrano, Peter Cherry
•Use first principles calculations to study the relationship between shape and size of nanoparticle and the oxygen adsorption energy.
• Investigate the effect of high oxygen coverage on the catalytic activity of the nanoparticles.

Advanced modelling for two-phase reacting flow
Edward Richardson (Investigator)
Engine designers want computer programs to help them invent ways to use less fuel and produce less pollution. This research aims to provide an accurate and practical model for the injection and combustion of liquid fuel blends.
BioSimGrid
Jonathan Essex, Hans Fangohr (Investigators), Richard Boardman, Syma Khalid, Steven Johnston
The aim of the BioSimGrid project is to make the results of large-scale computer simulations of biomolecules more accessible to the biological community. Such simulations of the motions of proteins are a key component in understanding how the structure of a protein is related to its dynamic function.
BRECcIA - Building REsearch Capacity for sustainable water and food security In sub-saharan Africa
The BRECcIA project is aimed at developing research and researchers to understand water and food security challenges in sub-Saharan Africa
Can we calculate the pKa of new drugs, based on their structure alone?
Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigator), Chris Pittock, Jacek Dziedzic
The pKa of an active compound in a pharmaceutical drug affects how it is absorbed and distributed around the human body. While there are various computational methods to predict pKa using only molecular structure data, these tend to be specialised to only one class of drug - we aim to generate a more generalised prediction method using quantum mechanics.

Centre for Doctoral Training in Next Generation Computational Modelling
Hans Fangohr, Ian Hawke, Peter Horak (Investigators), Susanne Ufermann Fangohr, Thorsten Wittemeier, Kieran Selvon, Alvaro Perez-Diaz, David Lusher, Ashley Setter, Emanuele Zappia, Hossam Ragheb, Ryan Pepper, Stephen Gow, Jan Kamenik, Paul Chambers, Robert Entwistle, Rory Brown, Joshua Greenhalgh, James Harrison, Jonathon Waters, Ioannis Begleris, Craig Rafter
The £10million Centre for Doctoral Training was launched in November 2013 and is jointly funded by EPSRC, the University of Southampton, and its partners.
The NGCM brings together world-class simulation modelling research activities from across the University of Southampton and hosts a 4-year doctoral training programme that is the first of its kind in the UK.

Designer 3D Magnetic Mesostructures
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Matteo Franchin, Andreas Knittel
A new electrodeposition self-assembly method allows for the growth of well defined mesostructures. This project's aim is to use this method in order to fabricate supraconducting and ferromagnetic mesostructures. Numerical methods based on well-established models are used in order to characterise the grown structures.

Development of a novel Navier-Stokes solver (HiPSTAR)
Richard Sandberg (Investigator)
Development of a highly efficient Navier-Stokes solver for HPC.

How far can we stretch the MARTINI?
Syma Khalid (Investigator), Ric Gillams
To date, coarse-grained lipid models have generally been parameterised to ensure the correct prediction of structural properties of membranes, such as the area per lipid and the bilayer thickness. The work described here explores the extent to which coarse-grained models are able to predict correctly bulk properties of lipids (phase behaviour) as well as the mechanical properties, such as lateral pressure profiles and stored elastic stress in bilayers. Such an evaluation is crucial for understanding the predictive capabilities of coarse-grained models.

Hybrid quantum and classical free energy methods in computational drug optimisation
Jonathan Essex, Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigators), Christopher Cave-Ayland
This work is based around the application of thermodynamics and quantum mechanics to the field of computational drug design and optimisation. Through the application of these theories the calculation of the physical properties of drug-like molecules is possible and hence some predictive power for their pharmaceutical activity in vivo can be obtained.
Immunotherapy Research: Modelling MHC Class I Complex Assembly
Timothy Elliott, Jorn Werner (Investigators), Alistair Bailey
This project uses mathematical modelling and simulation to investigate mechanisms by which our cells process and present biological information that is used by our immune system to distinguish between healthy and diseased cells.

Is fine-scale turbulence universal?
Richard Sandberg (Investigator), Patrick Bechlars
Complementary numerical simulations and experiments of various canonical flows will try to answer the question whether fine-scale turbulence is universal.

Jet noise
Richard Sandberg (Investigator), Neil Sandham
Direct numerical simulations are used to investigate jet noise.

Membrane-Protein Interactions: The Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria
Syma Khalid (Investigator), Pin-Chia Hsu
The aim of the project is to looking for the interaction sites, which may responsible for turning on/off activity in outer membrane protein with gram-negative bacteria membrane using molecular dynamic (MD) approach.
Molecular Fragments in Inhibitor Design
Jonathan Essex (Investigator), Michael Bodnarchuk
Fragment-Based Drug Discovery (FBDD) has emerged as an important tool in the drug discovery process. Instead of screening entire drug molecules, FBDD screens molecular fragments; constituents which make up drug molecules. A computational approach to identifying fragment binding is currently being sought which also yield binding free energy estimation.

Multi-scale simulations of bacterial outer-membrane proteins
Syma Khalid (Investigator), Jamie Parkin
Using Iridis to run multiple simulations, I aim to simulate the outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using X-ray crystal structures of proteins only recently resolved by Bert van den Berg, University of Massachusetts. By modelling the proteins in a realistic P. aeruginosa outer membrane, I aim to gain insight into the binding of these proteins to specific substrates and their function.
Multiscale modelling of biological membranes
Jonathan Essex (Investigator), Mario Orsi
Biological membranes are complex and fascinating systems, characterised by proteins floating in a sea of lipids. Biomembranes, besides being the fundamental structures employed by nature to encapsulate cells, play crucial roles in many phenomena indispensable for life, such as growth, energy storage, and in general information transduction via neural activity. In this project, we develop and apply multiscale computational models to simulate biological membranes and obtain molecular-level insights into fundamental structures and phenomena.
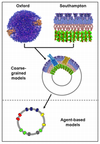
OMSys Towards a system model of a bacterial outer membrane
Syma Khalid (Investigator)
Many bacteria have an outer membrane which is the interface between the cell and its environment. The components of this membrane are well studied at an individual level, but there is a need to model and understand the outer membrane as a whole. In this project we aim to develop such a model of a bacterial outer membrane, linking computer simulations of the component molecules through to a more "systems biology" approach to modelling the outer membrane as a whole. Such an approach to modelling an OM must be multi-scale i.e. it must embrace a number of levels ranging from atomistic level modelling of e.g. the component proteins through to higher level "agent-based" modelling of the interplay of multiple components within the outer membrane as a whole. The different levels of description will be integrated to enable predictive modelling in order to explore the roles of outer membrane changes in e.g. antibiotic resistance.
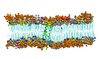
Probing the oligomeric state and interaction surface of Fukutin Transmembrane Domain in lipid bilayer via Molecular Dynamics simulations
Syma Khalid, Philip Williamson (Investigators), Daniel Holdbrook, Jamie Parkin, Nils Berglund, Yuk Leung
Fukutin Transmembrane Domain (FK1TMD) is localised to the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi Apparatus within the cell where it is believed to function as a glycosyltransferase. Its localisation within the cell is thought to be mediated by the interaction of its N-terminal transmembrane domain with the lipid bilayers surrounding these compartments, each of which possess a distinctive lipid composition. Studies have revealed that the N-terminal transmembrane domain of FK1TMD exists as dimer within dilauroylphosphatidylcholine bilayers and this interaction is driven by interactions between a characteristic TXXSS motif. Furthermore residues close to the N-terminus that have previously been shown to play a key role in the clustering of lipids are shown to play a key role in anchoring the protein in the membrane.

THE NORM MATE TRANSPORTER FROM N. GONORRHEAE: INSIGHTS INTO DRUG & ION BINDING FROM ATOMISTIC MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS
Syma Khalid (Investigator), Daniel Holdbrook, Thomas Piggot, Yuk Leung
The multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) transporters extrude a wide variety of substrates out of both mammalian and bacterial cells via the electrochemical gradient of protons and cations across the membrane. Multiple atomistic simulation are performed on a MATE transporter, NorM from Neisseria gonorrheae (NorM_NG) and NorM from Vibrio cholera (NorM_VC). These simulations have allowed us to identify the nature of the drug-protein/ion-protein interactions, and secondly determine how these interactions contribute to the conformational rearrangements of the protein.
People
 Timothy Elliott
Timothy ElliottProfessor, Medicine (FM)
 Jonathan Essex
Jonathan EssexProfessor, Chemistry (FNES)
 Hans Fangohr
Hans FangohrProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Richard Sandberg
Richard SandbergProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Neil Sandham
Neil SandhamProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Peter Horak
Peter HorakReader, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Jorn Werner
Jorn WernerReader, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Edward Richardson
Edward RichardsonSenior Lecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ian Hawke
Ian HawkeLecturer, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Chris-Kriton Skylaris
Chris-Kriton SkylarisLecturer, Chemistry (FNES)
 Syma Khalid
Syma KhalidPrincipal Research Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Richard Boardman
Richard BoardmanSenior Research Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Philip Williamson
Philip WilliamsonSenior Research Fellow, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Alistair Bailey
Alistair BaileyResearch Fellow, Medicine (FM)
 Jacek Dziedzic
Jacek DziedzicResearch Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Steven Johnston
Steven JohnstonResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Otello Roscioni
Otello RoscioniResearch Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Patrick Bechlars
Patrick BechlarsPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ioannis Begleris
Ioannis BeglerisPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Michael Bodnarchuk
Michael BodnarchukPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Rory Brown
Rory BrownPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Christopher Cave-Ayland
Christopher Cave-AylandPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Paul Chambers
Paul ChambersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Peter Cherry
Peter CherryPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Robert Entwistle
Robert EntwistlePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ric Gillams
Ric GillamsPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Stephen Gow
Stephen GowPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Joshua Greenhalgh
Joshua GreenhalghPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Harrison
James HarrisonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Leo Jofeh
Leo JofehPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Yuk Leung
Yuk LeungPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 David Lusher
David LusherPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Neil O'Brien
Neil O'BrienPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jamie Parkin
Jamie ParkinPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Alvaro Perez-Diaz
Alvaro Perez-DiazPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Chris Pittock
Chris PittockPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Craig Rafter
Craig RafterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Hossam Ragheb
Hossam RaghebPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Álvaro Ruiz-Serrano
Álvaro Ruiz-SerranoPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Kieran Selvon
Kieran SelvonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ashley Setter
Ashley SetterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Valerio Vitale
Valerio VitalePostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jonathon Waters
Jonathon WatersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Thorsten Wittemeier
Thorsten WittemeierPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Emanuele Zappia
Emanuele ZappiaPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petrina Butler
Petrina ButlerAdministrative Staff, Research and Innovation Services
 Susanne Ufermann Fangohr
Susanne Ufermann FangohrAdministrative Staff, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Stuart Curtis
Stuart CurtisAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Matteo Franchin
Matteo FranchinAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jan Kamenik
Jan KamenikAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Andreas Knittel
Andreas KnittelAlumnus, Industry
 Mario Orsi
Mario OrsiExternal Member, Queen Mary University of London
 Nils Berglund
Nils BerglundNone, None
 Daniel Holdbrook
Daniel HoldbrookNone, None
 Pin-Chia Hsu
Pin-Chia HsuNone, None
 Thomas Piggot
Thomas PiggotNone, None