Surface imaging
Surface Imaging
For queries about this topic, contact Graeme Earl.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects
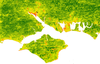
A novel method for monitoring air pollution from satellites at very high resolution
Joanna Nield, Jason Noble, Edward Milton (Investigators), Robin Wilson
Developing methods to monitor the clarity of the atmosphere from satellites at 100,000 times the resolution of previous methods. This can then be used to monitor air pollution, correct satellite images and provide data for climate studies. Simulation is used to model the effects of atmospheric pollution on light passing through the atmosphere, and to test the method under 'synthetic atmospheres'.

Advanced modelling for two-phase reacting flow
Edward Richardson (Investigator)
Engine designers want computer programs to help them invent ways to use less fuel and produce less pollution. This research aims to provide an accurate and practical model for the injection and combustion of liquid fuel blends.
Graphical Simulation of Archaeological Environments
Graeme Earl (Investigator)
This project defines an emerging area of interest in physically accurate rendering within the Archaeological Computing Research Group. Sub-projects include analysis of Roman spaces at herculaneum, Neolithic buildings at Catalhoyuk and simulation of a range of artefacts.
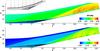
Laminar to Turbulent Transition in Hypersonic Flows
Neil Sandham, Heinrich Luedeke
Understanding of laminar to turbulent transition in hypersonic boundary-layer flows is crucial for re-entry vehicle design and optimization. The boundary-layer state directly affects the temperatures on the vehicle surface and its viscous drag. Therefore transition has to be considered to correctly compensate for drag and to properly design the thermal protection system.
For the proposed study, in order to obtain a clear understanding of the transition process, the configuration is kept as simple as possible by varying only a minimum number of parameters affecting transition on a simple test geometry such as a swept ramp at different sweep angles. To investigate the influence of such sweep angles on the transition process in the hypersonic regime, Direct Numerical Simulations (DNS) of the turbulent flow field are carried out on the Iridis cluster.

Life assessment methods for industrial steam turbine blade to disc interfaces
Katherine Soady (Investigator)
This is an EngD project sponsored by E.ON New Build and Technology Ltd. which aims to develop the methods currently implemented in life assessment of industrial steam turbine blade to disc interfaces to take account of the surface treatment process (shot peening) which is applied to component before service and after repair.

MXL Project
Mark Taylor, Junfen Shi (Investigators)
‘MXL’ is short for “Enhanced patient safety by computational Modelling from clinically available X-rays to minimise the risk of overload and instability for optimised function and Longevity”. This is an international EU-funded project which the Bioengineering Sciences Research Group at Southampton is involved in. For more information, visit http://www.m-x-l.eu
Statistical model of the knee
Mark Taylor (Investigator), Francis Galloway, Prasanth Nair
Development of methods for large scale computational testing of a tibial tray incorporating inter-patient variability.
The application of automated pattern metrics to surface moisture influences on modelled dune field development
Robin Wilson, Joanna Nield (Investigators)
Areas of sand dunes (known as dunefields) develop complex patterns over time. These are influenced by both the past and present environmental conditions, including surface moisture, vegetation distribution and human impact. This project develops a method of automated pattern analysis which allow the patterns produced by a large number of sand dune evolution simulations (performed using the DECAL model) to be quantified over time.

µ-VIS Computed Tomography Centre
Ian Sinclair, Richard Boardman, Dmitry Grinev, Philipp Thurner, Simon Cox, Jeremy Frey, Mark Spearing, Kenji Takeda (Investigators)
A dedicated centre for computed tomography (CT) at Southampton, providing complete support for 3D imaging science, serving Engineering, Biomedical, Environmental and Archaeological Sciences. The centre encompasses five complementary scanning systems supporting resolutions down to 200nm and imaging volumes in excess of one metre: from a matchstick to a tree trunk, from an ant's wing to a gas turbine blade.
People
 Simon Cox
Simon CoxProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jeremy Frey
Jeremy FreyProfessor, Chemistry (FNES)
 Edward Milton
Edward MiltonProfessor, Geography (FSHS)
 Neil Sandham
Neil SandhamProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ian Sinclair
Ian SinclairProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Mark Spearing
Mark SpearingProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Mark Taylor
Mark TaylorProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Tiina Roose
Tiina RooseReader, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Thomas Blumensath
Thomas BlumensathSenior Lecturer, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Graeme Earl
Graeme EarlSenior Lecturer, Humanities (FH)
 Prasanth Nair
Prasanth NairSenior Lecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Edward Richardson
Edward RichardsonSenior Lecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Fraser Sturt
Fraser SturtSenior Lecturer, Humanities (FH)
 Mohamed Bakoush
Mohamed BakoushLecturer, Management (FBL)
 Philipp Thurner
Philipp ThurnerLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Richard Boardman
Richard BoardmanSenior Research Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Reno Choi
Reno ChoiSenior Research Fellow, Geography (FSHS)
 Felipe Alves Portela
Felipe Alves PortelaResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petros Bogiatzis
Petros BogiatzisResearch Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Dmitry Grinev
Dmitry GrinevResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Heinrich Luedeke
Heinrich LuedekeResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jason Noble
Jason NobleResearch Fellow, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Robin Wilson
Robin WilsonResearch Fellow, Geography (FSHS)
 Leonidas Bourikas
Leonidas BourikasPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Caroline Duignan
Caroline DuignanPostgraduate Research Student, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Francis Galloway
Francis GallowayPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stephen Powell
Stephen PowellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Álvaro Ruiz-Serrano
Álvaro Ruiz-SerranoPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Katherine Soady
Katherine SoadyPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petrina Butler
Petrina ButlerAdministrative Staff, Research and Innovation Services
 Arthur Lugtigheid
Arthur LugtigheidAlumnus, Psychology (FSHS)
 Kenji Takeda
Kenji TakedaAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Daisuke Sasaki
Daisuke SasakiNone, None
 Junfen Shi
Junfen ShiNone, None