Wave propagation

Waves are disturbances that propagate through space and time. Examples include mechanical waves in solid and fluids (water waves, sound and vibrations), electromagnetic waves (light, radio waves, etc.), gravitational waves. This topic covers any work aiming to understand and/or predict the interference between multiple waves, scattering by obstacles, and refraction by inhomogeneities. Applications are found in many areas of science and engineering, for instance astrophysics, biomedical applications, acoustical engineering, ship science, etc. For more information see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave
For queries about this topic, contact Gwenael Gabard.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects
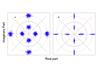
All-Optical Phase Regeneration of Fiber Optic Communication Signals
Peter Horak (Investigator), Graham Hesketh
All-optical phase regeneration uses a process known as four-wave mixing in a nonlinear optical fiber to carefully mix light with a communication signal in such a way that it cancels transmission noise in the the signals phase, increasing the distance over which the signal can be transmitted. New regenerator designs are presented that suppress phase to amplitude noise conversion and performance is simulated using a supercomputer to assist experimental investigation.

Centre for Doctoral Training in Next Generation Computational Modelling
Hans Fangohr, Ian Hawke, Peter Horak (Investigators), Susanne Ufermann Fangohr, Thorsten Wittemeier, Kieran Selvon, Alvaro Perez-Diaz, David Lusher, Ashley Setter, Emanuele Zappia, Hossam Ragheb, Ryan Pepper, Stephen Gow, Jan Kamenik, Paul Chambers, Robert Entwistle, Rory Brown, Joshua Greenhalgh, James Harrison, Jonathon Waters, Ioannis Begleris, Craig Rafter
The £10million Centre for Doctoral Training was launched in November 2013 and is jointly funded by EPSRC, the University of Southampton, and its partners.
The NGCM brings together world-class simulation modelling research activities from across the University of Southampton and hosts a 4-year doctoral training programme that is the first of its kind in the UK.
Computational Methods for Aircraft Noise Prediction
Gwenael Gabard (Investigator), Albert Prinn
The aim of this project is to develop and test an efficient flow acoustics solver based on the finite element method and the potential flow theory.
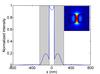
Continuously Tunable Optical Buffer
Peter Horak (Investigator)
The project aims to design, fabricate and test a novel integrated all-optical buffer device that is based on MEMS technology and provides a continuously tunable delay for optical pulses over a broad wavelength region. Such a device could play a crucial role in future packet-switched optical networks, photonic integrated circuits and coherent light based applications such as optically steered phase array antennas, LIDAR and optical coherence tomography.
This EPSRC funded project is a collaboration between the Optoelectronics Research Centre, Southampton, and University College London.

Dynamag: computational magnonics
Hans Fangohr, Atul Bhaskar (Investigators), Matteo Franchin, Andreas Knittel
Analytical treatment of long range magneto-dipole interactions is a bottle-neck of magnonics and more generally of the theory of spin waves in non-uniform media. This project develops a theoretical framework for analysis of magnonic phenomena in magnetic nano-structures, including isolated nano-elements, arrays of those, and extended magnonic crystals. The DYNAMAG project is funded by the EU FP7 and the DST of India.

How sensitive is ocean model utility to resolution?
Kevin Oliver (Investigator), Maike Sonnewald
One of the most intriguing problems in recent ocean modeling research is the impact of varying model resolution on model accuracy. Increasing model resolution one includes more of the important processes. However, the increase in accuracy with resolution is unlikely to be linear. Thus, as computational cost increases with resolution, a critical assessment of achieved benefits is prudent. Here we analyse a suite of realistic and compatible global ocean model runs from coarse (1o, ORCA1), eddy-permitting (1/4o, ORCA025) and eddy resolving (1/12o, ORCA12) resolutions. Comparisons of steric height variability (varSH) highlight changes in ocean density structure, revealing impacts on mechanisms such as downwelling and eddy energy dissipation. We assess vertical variability using the covariace of the deep and shallow varSH. Together with assessing isopycnal movements, we demonstrate the influence of deep baroclinic modes and regions where the barotropic flow sheds eddies. Significant changes in the deepwater formation and dispersion both in the Arctic and Antarctic are found between resolutions. The varSH increased from ORCA1 to ORCA025 and ORCA12, particularily in the Southern Ocean and Western Boundary Currents. However, there is no significant covariance between the surface and deep in ORCA1, while ORCA025 and ORCA12 show significant covariance, implying an important missing energy pathway in ORCA1. Comparing ORCA025 and ORCA12 we see significant differences in eddy energy dissipation. We assess the impact of varying model resolution on the mean flow, discussing implications to dissipation pathways on model accuracy, with reference to stochastic parameterisation schemes.
Investigation of acoustic radiation forces on micro-particles and cells in ultrasonic particle manipulation
Martyn Hill (Investigator), Puja Mishra
A Finite Element model is developed to investigate the force generated on a particle of arbitrary geometry and composition in a sound field. The model overcame the drawbacks of existing analytical solutions of size restriction and provided the flexibility of particle representation. This suggested useful results on shape dependency, effect of elasticity of particle and dominancy of nucleus in a cell in estimating the force on a single particle.

Optical Characterisation of Black Silicon for Photovoltaics Using the Finite Element Method
Jack Tyson (Investigator)
Here we present a novel method of simulating the reflectance spectra of black silicon solar cells using the finite element method. Designed in COMSOL Multiphysics is a new set of algorithm-controlled-geometries rendering a vast array of different structural permutations of silicon nanowires. Our model focused on the variation of this geometry within customisable predefined conditions in large output quantities, collated and averaged to reliably determine the reflectance of an entire black silicon solar cell.
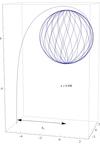
Self-Force and Black Hole Inspirals
Sam Dolan (Investigator)
We use IRIDIS to compute the self-force acting on a solar-mass black hole orbiting a supermassive black hole.
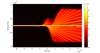
Soft x-ray science on a tabletop
Peter Horak, Jeremy Frey, Bill Brocklesby (Investigators), Patrick Anderson, Arthur Degen-Knifton
Complex numerical simulations are being performed to aid experimentalists at Southampton realize the next generation of high brightness tabletop sources of coherent soft x-rays.?

Today's Computation Enabling Tomorrow's Seamless Communication
Lajos Hanzo (Investigator), Varghese Thomas
Radio Over Fibre (ROF) is a communication technique that aims to gainfully amalgamate the benefits of optical and wireless communication, while keeping the system cost low. This technique would support the next generation of wireless services.
People
 Hans Fangohr
Hans FangohrProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jeremy Frey
Jeremy FreyProfessor, Chemistry (FNES)
 Lajos Hanzo
Lajos HanzoProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Martyn Hill
Martyn HillProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Janne Ruostekoski
Janne RuostekoskiProfessor, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Richard Sandberg
Richard SandbergProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Bill Brocklesby
Bill BrocklesbyReader, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Peter Horak
Peter HorakReader, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Atul Bhaskar
Atul BhaskarSenior Lecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Neil Broderick
Neil BroderickLecturer, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Gwenael Gabard
Gwenael GabardLecturer, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Ian Hawke
Ian HawkeLecturer, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Kevin Oliver
Kevin OliverLecturer, National Oceanography Centre (FNES)
 Anatoliy Vorobev
Anatoliy VorobevLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Rie Sugimoto
Rie SugimotoSenior Research Fellow, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Petros Bogiatzis
Petros BogiatzisResearch Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Nicola De Tullio
Nicola De TullioResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Sam Dolan
Sam DolanResearch Fellow, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Patrick Anderson
Patrick AndersonPostgraduate Research Student, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Patrick Bechlars
Patrick BechlarsPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ioannis Begleris
Ioannis BeglerisPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 ThankGod E. Boye
ThankGod E. BoyePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Rory Brown
Rory BrownPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Paul Chambers
Paul ChambersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alicia Costalago Meruelo
Alicia Costalago MerueloPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 Robert Entwistle
Robert EntwistlePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stephen Gow
Stephen GowPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Joshua Greenhalgh
Joshua GreenhalghPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Harrison
James HarrisonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Graham Hesketh
Graham HeskethPostgraduate Research Student, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Guy Jacobs
Guy JacobsPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Edwin Lizarazo
Edwin LizarazoPostgraduate Research Student, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Justin Lovegrove
Justin LovegrovePostgraduate Research Student, Mathematics (FSHS)
 David Lusher
David LusherPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Juraj Mihalik
Juraj MihalikPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Puja Mishra
Puja MishraPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alvaro Perez-Diaz
Alvaro Perez-DiazPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Craig Rafter
Craig RafterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Hossam Ragheb
Hossam RaghebPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Kieran Selvon
Kieran SelvonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ashley Setter
Ashley SetterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Maike Sonnewald
Maike SonnewaldPostgraduate Research Student, National Oceanography Centre (FNES)
 Stefano Spagnolo
Stefano SpagnoloPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jack Tyson
Jack TysonPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jonathon Waters
Jonathon WatersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Thorsten Wittemeier
Thorsten WittemeierPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Emanuele Zappia
Emanuele ZappiaPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petrina Butler
Petrina ButlerAdministrative Staff, Research and Innovation Services
 Susanne Ufermann Fangohr
Susanne Ufermann FangohrAdministrative Staff, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Matteo Franchin
Matteo FranchinAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 basel haji
basel hajiAlumnus, University of lattakia
 Jan Kamenik
Jan KamenikAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Kondwani Kanjere
Kondwani KanjereAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Andreas Knittel
Andreas KnittelAlumnus, Industry
 John Muddle
John MuddleAlumnus, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Albert Prinn
Albert PrinnAlumnus, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Arthur Degen-Knifton
Arthur Degen-KniftonNone, None
 Varghese Thomas
Varghese ThomasNone, None