Finite elements
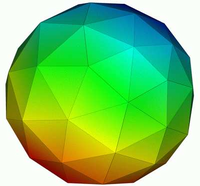
The finite element method (often called finite element analysis when used in applications) in is a widespread tool that discretises space into smaller parts of varying shapes (including tetrahedra), and is used to solve partial differential equations (PDEs). The method approximates the PDE with a system of algebraic equations for steady state problems, a system of ordinary differential equations for transient problems.
Image: approximation of a sphere with a set of tetrahedra (known as mesh or grid).
For queries about this topic, contact Hans Fangohr.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects

Centre for Doctoral Training in Next Generation Computational Modelling
Hans Fangohr, Ian Hawke, Peter Horak (Investigators), Susanne Ufermann Fangohr, Thorsten Wittemeier, Ashley Setter, Kieran Selvon, Hossam Ragheb, Craig Rafter, Alvaro Perez-Diaz, Ryan Pepper, David Lusher, Stephen Gow, James Harrison, Paul Chambers, Jan Kamenik, Ioannis Begleris, Robert Entwistle, Jonathon Waters, Rory Brown, Joshua Greenhalgh, Emanuele Zappia
The £10million Centre for Doctoral Training was launched in November 2013 and is jointly funded by EPSRC, the University of Southampton, and its partners.
The NGCM brings together world-class simulation modelling research activities from across the University of Southampton and hosts a 4-year doctoral training programme that is the first of its kind in the UK.

Chaotic Analysis of Partial Discharge
Paul Lewin (Investigator), Lyuboslav Petrov
The deterministic character of PD pulses predicted by theory has been shown to be existent for certain PD events. Finding characteristic patterns in phase space enables field-data PD detection with high reliability.
Computational Methods for Aircraft Noise Prediction
Gwenael Gabard (Investigator), Albert Prinn
The aim of this project is to develop and test an efficient flow acoustics solver based on the finite element method and the potential flow theory.
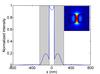
Continuously Tunable Optical Buffer
Peter Horak (Investigator)
The project aims to design, fabricate and test a novel integrated all-optical buffer device that is based on MEMS technology and provides a continuously tunable delay for optical pulses over a broad wavelength region. Such a device could play a crucial role in future packet-switched optical networks, photonic integrated circuits and coherent light based applications such as optically steered phase array antennas, LIDAR and optical coherence tomography.
This EPSRC funded project is a collaboration between the Optoelectronics Research Centre, Southampton, and University College London.
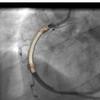
Coronary Artery Stent Design for Challenging Disease
Neil Bressloff (Investigator), Georgios Ragkousis
In this work, a method has been setup to (i) reconstruct diseased patient specific coronary artery segments; (ii) use the new supercomputer to run many simulations of this complex problem and (iii) assess the degree of stent malapposition. The aim now is to devise a stent delivery system that can mitigate this problem
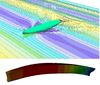
Coupled Fluid-Structure Interaction to model Three-Dimensional Dynamic Behaviour of Ships in Waves
Pandeli Temarel, Zhi-Min Chen (Investigators), Puram Lakshmynarayanana
In the present study we focus our attention on fluid-structure interactions (FSI) of flexible marine structures in waves by coupling a fluid solver using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and a structural solver using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software.
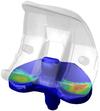
DePuy Technology Partnership
Mark Taylor (Investigator), Adam Briscoe
This initiative concerns the transfer of knowledge between three key institutions (University of Southampton, University of Leeds and University of Hamburg) and DePuy International limited. The project is concerned with the ongoing advancement of technology used in orthopaedic devices.

Designer 3D Magnetic Mesostructures
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Matteo Franchin, Andreas Knittel
A new electrodeposition self-assembly method allows for the growth of well defined mesostructures. This project's aim is to use this method in order to fabricate supraconducting and ferromagnetic mesostructures. Numerical methods based on well-established models are used in order to characterise the grown structures.
Dynamics of interacting magnetic nanoparticles
Thomas Fischbacher (Investigator), Maximilian Albert
The project aims at extending the micromagnetic simulation framework 'nmag' developed at the University of Southampton to enable it to handle dynamic geometries. The extended framework will then be used to study systems such as interacting magnetic nanoparticles.
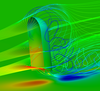
Fluid Structure Interactions of Yacht Sails
Stephen Turnock (Investigator), Daniele Trimarchi
The research is the main subject of the PhD topic. It regards the application of fluid structure interaction techniques to the domain of yacht sails simulation
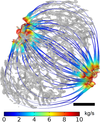
Image Based Modelling of Fluid Flow through Lymph Nodes
Tiina Roose, Bharathram Ganapathisubramani, Geraldine Clough (Investigators), Laura Cooper
In this project we are using images of mouse lymph nodes to investigate the fluid transport pathways through it. The images of the nodes are taken using selective plane illumination microscopy, and synchrotron micro computed tomography. The fluid flow is modelled using Darcy's law in COMSOL Multiphysics and the models are run on the Iridis cluster.
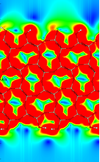
Investigation into the Interfacial Physics of Field Effect Biosensors
Nicolas Green, Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigators), Benjamin Lowe
This interdisciplinary research aims to improve understanding of Field Effect Transistor Biosensors (Bio-FETs) and to work towards a multiscale model which can be used to better understand and predict device response.

Investigations of Lymphatic Fluid Flow
Tiina Roose, Bharathram Ganapathisubramani, Geraldine Clough (Investigators), Laura Cooper
The lymphatic system performs three main roles returns interstitial fluid back into the blood stream to maintain tissue fluid homeostasis. The aim of this project is to increase our understanding of how the lymph flows through the system by creating three dimensional fluid structure interaction models of the secondary lymphatic valves and image based models of lymph nodes.

Life assessment methods for industrial steam turbine blade to disc interfaces
Katherine Soady (Investigator)
This is an EngD project sponsored by E.ON New Build and Technology Ltd. which aims to develop the methods currently implemented in life assessment of industrial steam turbine blade to disc interfaces to take account of the surface treatment process (shot peening) which is applied to component before service and after repair.
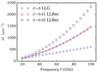
Magnetic dynamics under the Landau-Lifshitz-Baryakhtar equation
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Weiwei Wang
Magnetic dynamics using the Landau-Lifshitz-Baryakhtar (LLBar) equation that the nonlocal damping is included as well as the scalar Gilbert damping.
Mathematical modelling of plant nutrient uptake
Tiina Roose (Investigator)
In this project I will describe a model of plant water and nutrient uptake and how to translate this model and experimental data from the single root scale to the root branching structure scale.
Micromagnetic simulation of Magnetoelectric Multiferroics
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Rebecca Carey
The focus of this project is towards the understanding of the magnetic and electric couplings in multiferroic materials, in order to create a magnetoelectric micromagnetic model.
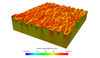
Microstructural modeling of skin mechanics
Georges Limbert (Investigator), Emanuele Zappia
Microstructural modeling of skin mechanics to gain a mechanistic insight into the biomechanics of the skin.

Modelling the Combined Effects of Total Ionizing Dose and Random Dopant Fluctuations in sub-100 nm gate-length Transistors
Kees de Groot (Investigator), Eleni Chatzikyriakou
The radiation hardness of state-of-the-art silicon-on-insulator transistors of gate length dimensions of 90 nm and beyond is investigated. The combined effects of oxide charges and random fluctuations of the dopant atoms in silicon are considered. It is demonstrated that a parasitic channel forms at the interface of buried oxide and shallow trench isolation regions of the device and that this effect is aggravated by random dopant fluctuations.
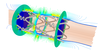
Multi-objective design optimisation of coronary stents
Neil Bressloff, Georges Limbert (Investigators), Sanjay Pant
Stents are tubular type scaffolds that are deployed (using an inflatable balloon on a catheter), most commonly to recover the shape of narrowed (diseased) arterial segments. Despite the widespread clinical use of stents in cardiovascular intervention, the presence of such devices can cause adverse responses leading to fatality or to the need for further treatment. The most common unwanted responses of inflammation are in-stent restenosis and thrombosis. Such adverse biological responses in a stented artery are influenced by many factors, including the design of the stent. This project aims at using multi-objective optimisation techniques to find an optimum family of coronary stents which are more resistant to the processes of in-stent restenosis (IR) and stent thrombosis (ST).
Multiscale Modelling of Cellular Calcium Signalling
Hans Fangohr, Jonathan Essex (Investigators), Dan Mason
Calcium ions play a vitally important role in signal transduction and are key to many cellular processes including muscle contraction and cell apoptosis (cell death). This importance has made calcium an active area in biomedical science and mathematical modelling.

Multiscale Relativistic Simulations
Ian Hawke (Investigator), Alex Wright
There has been recent success in experiments, such as LIGO, in detecting the mergers of celestial objects via the gravitational waves they emit. By implementing numerical methods, we aim to speed up the numerical simulations of these events but up to two orders of magnitudes, and study binary inspirals in greater detail and over much larger timespans.

Multiscale Relativistic Simulations
There has been recent success in experiments, such as LIGO, in detecting the mergers of celestial objects via the gravitational waves they emit. I will use numerical methods to simulate the inspiral of a black hole/neutron star binary system.

MXL Project
Mark Taylor, Junfen Shi (Investigators)
‘MXL’ is short for “Enhanced patient safety by computational Modelling from clinically available X-rays to minimise the risk of overload and instability for optimised function and Longevity”. This is an international EU-funded project which the Bioengineering Sciences Research Group at Southampton is involved in. For more information, visit http://www.m-x-l.eu
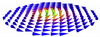
Nmag - computational micromagnetics
Hans Fangohr, Thomas Fischbacher (Investigators), Matteo Franchin, Andreas Knittel, Maximilian Albert, Dmitri Chernyshenko, Massoud Najafi, Richard Boardman
Nmag is a micromagnetic simulation package based on the general purpose multi-physics library nsim. It is developed by the group of Hans Fangohr and Thomas Fischbacher in the School of Engineering Sciences at the University of Southampton and released under the GNU GPL.
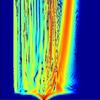
Nonlinear Optical Pulse Propagation
Peter Horak, Francesco Poletti (Investigators)
The work is concerned with the propagation of high-power short-pulse propagation in microstructured fibres or waveguides. Dispersion properties and optical nonlinearities are exploited for pulse shaping techniques in space, time, and frequency. Investigated microstructures include silica or soft-glass templates, gas-filled capillaries, and semiconductor-filled fibres, and optical wavelengths range from the X-ray to the mid-infrared regime.
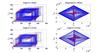
On the applicability of nonlinear timeseries methods for partial discharge analysis
Paul Lewin (Investigator), Lyuboslav Petrov
The governing processes of Partial Discharge (PD)
phenomena trigger aperiodic chains of events resulting in ’ap-
parently’ stochastic data, for which the widely adopted analysis
methodology is of statistical nature. However, it can be shown,
that nonlinear analysis methods can prove more adequate in
detecting certain trends and patterns in complex PD timeseries.
In this work, the application of nonlinear invariants and phase
space methods for PD analysis are discussed and potential pitfalls
are identified. Unsupervised statistical inference techniques based
on the use of surrogate data sets are proposed and employed for
the purpose of testing the applicability of nonlinear algorithms
and methods. The Generalized Hurst Exponent and Lempel Ziv
Complexity are used for finding the location of the system under
test on the spectrum between determinism and stochasticity. The
algorithms are found to have strong classification abilities at
discerning between surrogates and original point series, giving
motivation for further investigations.

Optical Characterisation of Black Silicon for Photovoltaics Using the Finite Element Method
Jack Tyson (Investigator)
Here we present a novel method of simulating the reflectance spectra of black silicon solar cells using the finite element method. Designed in COMSOL Multiphysics is a new set of algorithm-controlled-geometries rendering a vast array of different structural permutations of silicon nanowires. Our model focused on the variation of this geometry within customisable predefined conditions in large output quantities, collated and averaged to reliably determine the reflectance of an entire black silicon solar cell.
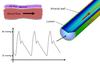
Preventing Alzheimer's Disease: A Multiphysics Simulation Approach
Neil Bressloff, Giles Richardson, Roxana-Octavia Carare (Investigators), Alexandra Diem
Experimental research has identified the causes of many diseases, such as Alzheimer's Disease. However, finding an effective treatment is very cost- and time-intensive and sacrifices many animals and does not guarantee success. In this PhD project, we investigate the driving force of solute drainage in the brain using multiphysics simulations in order to identify possible ways of preventing dementia.
Pushing the Envelope of Planetary Formation and Evolution Simulations
Peter Bartram
A full understanding of the formation and the early evolution of the Solar System and extrasolar planetary systems ranks among natural science's grand challenges, and at present, even the dominant processes responsible for generating the observed planetary architecture remain elusive.
Respiratory mask modeling
Jacques Ernes
Abaqus modelling of repiratory masks, bioengineering, Health sciences
Simulating the Write Process in Perpendicular Magnetic Media
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Stuart Curtis
The project aims to use Nmag, a micromagnetics software package developed by the CMG to model the writing process in perpendicular magnetic recording.

Simulations of Magnetic Skyrmions
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Ryan Pepper
The manipulation of magnetic skyrmions could prove to be a useful technique for storing data on an unprecedented density scale. In this project we seek to better understand their properties and ways to control them.
Skyrmionic states in confined nanostructures
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Marijan Beg
An ever increasing need for data storage creates great challenges for the development of high-capacity storage devices that are cheap, fast, reliable, and robust. Because of the fundamental constraints of today's technologies, further progress requires radically different approaches. Magnetic skyrmions are very promising candidates for the development of future low-power, high-capacity, non-volatile data storage devices.
Stability of chiral structures in magnetic nanodisks
Hans Fangohr, Weiwei Wang (Investigators), David Cortes
This project is aimed to study the stability of skyrmionic and helical equilibrium states in magnetic nanodisks, using computational simulations.
Statistical model of the knee
Mark Taylor (Investigator), Francis Galloway, Prasanth Nair
Development of methods for large scale computational testing of a tibial tray incorporating inter-patient variability.
Tissue Engineering
Tiina Roose (Investigator)
This project deals with applying mathematical and computational modelling techniques to answer questions that are useful for tissue engineering applications.

Wave-based discontinuous Galerkin methods
Gwenael Gabard (Investigator), Greg Kennedy
Wave-based computational methods are developed to model sound propagation in moving inhomogeneous media.

µ-VIS Computed Tomography Centre
Ian Sinclair, Richard Boardman, Dmitry Grinev, Philipp Thurner, Simon Cox, Jeremy Frey, Mark Spearing, Kenji Takeda (Investigators)
A dedicated centre for computed tomography (CT) at Southampton, providing complete support for 3D imaging science, serving Engineering, Biomedical, Environmental and Archaeological Sciences. The centre encompasses five complementary scanning systems supporting resolutions down to 200nm and imaging volumes in excess of one metre: from a matchstick to a tree trunk, from an ant's wing to a gas turbine blade.
People
 Neil Bressloff
Neil BressloffProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Geraldine Clough
Geraldine CloughProfessor, Medicine (FM)
 Simon Cox
Simon CoxProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Kees de Groot
Kees de GrootProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jonathan Essex
Jonathan EssexProfessor, Chemistry (FNES)
 Hans Fangohr
Hans FangohrProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jeremy Frey
Jeremy FreyProfessor, Chemistry (FNES)
 Bharathram Ganapathisubramani
Bharathram GanapathisubramaniProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Paul Lewin
Paul LewinProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Ian Sinclair
Ian SinclairProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Mark Spearing
Mark SpearingProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Mark Taylor
Mark TaylorProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Pandeli Temarel
Pandeli TemarelProfessor, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Stephen Turnock
Stephen TurnockProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Nicolas Green
Nicolas GreenReader, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Peter Horak
Peter HorakReader, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Tobias Keller
Tobias KellerReader, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Giles Richardson
Giles RichardsonReader, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Tiina Roose
Tiina RooseReader, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Roxana-Octavia Carare
Roxana-Octavia CarareSenior Lecturer, Medicine (FM)
 Prasanth Nair
Prasanth NairSenior Lecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Edward Richardson
Edward RichardsonSenior Lecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Zhi-Min Chen
Zhi-Min ChenLecturer, Chemistry (FNES)
 Gwenael Gabard
Gwenael GabardLecturer, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Ian Hawke
Ian HawkeLecturer, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Georges Limbert
Georges LimbertLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Chris-Kriton Skylaris
Chris-Kriton SkylarisLecturer, Chemistry (FNES)
 Philipp Thurner
Philipp ThurnerLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Richard Boardman
Richard BoardmanSenior Research Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Francesco Poletti
Francesco PolettiSenior Research Fellow, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Rie Sugimoto
Rie SugimotoSenior Research Fellow, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Felipe Alves Portela
Felipe Alves PortelaResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petros Bogiatzis
Petros BogiatzisResearch Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Adam Briscoe
Adam BriscoeResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Dmitry Grinev
Dmitry GrinevResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Nina Podoliak
Nina PodoliakResearch Fellow, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Maximilian Albert
Maximilian AlbertPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Peter Bartram
Peter BartramPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 Patrick Bechlars
Patrick BechlarsPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ioannis Begleris
Ioannis BeglerisPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Leonidas Bourikas
Leonidas BourikasPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Rory Brown
Rory BrownPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Jamie Caldwell
Jamie CaldwellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Rebecca Carey
Rebecca CareyPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Paul Chambers
Paul ChambersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Eleni Chatzikyriakou
Eleni ChatzikyriakouPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Dmitri Chernyshenko
Dmitri ChernyshenkoPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Laura Cooper
Laura CooperPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 David Cortes
David CortesPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Enrique Cuan-Urquizo
Enrique Cuan-UrquizoPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alexandra Diem
Alexandra DiemPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Samuel Diserens
Samuel DiserensPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Robert Entwistle
Robert EntwistlePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Francis Galloway
Francis GallowayPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stephen Gow
Stephen GowPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Joshua Greenhalgh
Joshua GreenhalghPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Harrison
James HarrisonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alex James
Alex JamesPostgraduate Research Student, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Greg Kennedy
Greg KennedyPostgraduate Research Student, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Puram Lakshmynarayanana
Puram LakshmynarayananaPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Justin Lovegrove
Justin LovegrovePostgraduate Research Student, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Benjamin Lowe
Benjamin LowePostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 David Lusher
David LusherPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Sam Mangham
Sam ManghamPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Juraj Mihalik
Juraj MihalikPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Puja Mishra
Puja MishraPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Sanjay Pant
Sanjay PantPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alvaro Perez-Diaz
Alvaro Perez-DiazPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Lyuboslav Petrov
Lyuboslav PetrovPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Daniel Powell
Daniel PowellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stephen Powell
Stephen PowellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Craig Rafter
Craig RafterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Hossam Ragheb
Hossam RaghebPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Georgios Ragkousis
Georgios RagkousisPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Christoph Riedel
Christoph RiedelPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Álvaro Ruiz-Serrano
Álvaro Ruiz-SerranoPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Kieran Selvon
Kieran SelvonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ashley Setter
Ashley SetterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Katherine Soady
Katherine SoadyPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alex Stuikys
Alex StuikysPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Daniele Trimarchi
Daniele TrimarchiPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jack Tyson
Jack TysonPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Valerio Vitale
Valerio VitalePostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jonathon Waters
Jonathon WatersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Thorsten Wittemeier
Thorsten WittemeierPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Martin Wood
Martin WoodPostgraduate Research Student, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Alex Wright
Alex WrightPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Emanuele Zappia
Emanuele ZappiaPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petrina Butler
Petrina ButlerAdministrative Staff, Research and Innovation Services
 Susanne Ufermann Fangohr
Susanne Ufermann FangohrAdministrative Staff, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Erika Quaranta
Erika QuarantaEnterprise staff, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stuart Curtis
Stuart CurtisAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Thomas Fischbacher
Thomas FischbacherAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Matteo Franchin
Matteo FranchinAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 basel haji
basel hajiAlumnus, University of lattakia
 Jan Kamenik
Jan KamenikAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Andreas Knittel
Andreas KnittelAlumnus, Industry
 Dan Mason
Dan MasonAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Massoud Najafi
Massoud NajafiAlumnus, Arbeitsbereich Technische Informatik Systeme, University of Hamburg, Germany
 Albert Prinn
Albert PrinnAlumnus, Institute of Sound & Vibration Research (FEE)
 Kenji Takeda
Kenji TakedaAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Weiwei Wang
Weiwei WangAlumnus, Ningbo University
 Marijan Beg
Marijan BegExternal Member, Imperial College London
 Jacques Ernes
Jacques ErnesExternal Member, Technical University of Eindhoven
 Daisuke Sasaki
Daisuke SasakiNone, None
 Junfen Shi
Junfen ShiNone, None