Git
Git is a distributed version control system.
Some useful documentation can be found on the Git website. For those familiar with SVN this guide may be useful.
For queries about this topic, contact Quintin Hill.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects
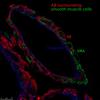
A Mathematical Analysis of the Driving Force of Perivascular Drainage in the Brain
Giles Richardson, Roxana-Octavia Carare (Investigators), Alexandra Diem
The observation that solute drainage in the brain occurs in the reverse direction of the blood flow has for a long time been puzzling for researchers. We developed a simple analytical model that can explain this reverse drainage of solutes and has potential implications for the development of treatment for Alzheimer's Disease.
A novel method for monitoring air pollution from satellites at very high resolution
Joanna Nield, Jason Noble, Edward Milton (Investigators), Robin Wilson
Developing methods to monitor the clarity of the atmosphere from satellites at 100,000 times the resolution of previous methods. This can then be used to monitor air pollution, correct satellite images and provide data for climate studies. Simulation is used to model the effects of atmospheric pollution on light passing through the atmosphere, and to test the method under 'synthetic atmospheres'.

Ab initio simulations of chemical reactions on platinum nanoparticles
Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigator), Álvaro Ruiz-Serrano, Peter Cherry
•Use first principles calculations to study the relationship between shape and size of nanoparticle and the oxygen adsorption energy.
• Investigate the effect of high oxygen coverage on the catalytic activity of the nanoparticles.
Automatic Image Retrieval with Soft Biometrics for Surveillance
Mark Nixon, John Carter (Investigators), Daniel Martinho-Corbishley
We're investigating ways to automatically describe and identify pedestrians from surveillance footage using human understandable, soft biometric labels. Our goal is to enable surveillance operators to search for pedestrians in a video network using soft biometric descriptions, and to automatically retrieve these descriptions from CCTV images.

B-meson coupling with relativistic heavy quarks
Jonathan Flynn (Investigator), Ben Samways, Dirk Broemmel, Patrick Fritzsch
We non-perturbatively compute the coupling between B* and B pi meson states relying on relativistic heavy quarks and domain wall light fermions. The coupling is of importance for an effective description of hadronic heavy meson decays.
BRECcIA - Building REsearch Capacity for sustainable water and food security In sub-saharan Africa
The BRECcIA project is aimed at developing research and researchers to understand water and food security challenges in sub-Saharan Africa

Centre for Doctoral Training in Next Generation Computational Modelling
Hans Fangohr, Ian Hawke, Peter Horak (Investigators), Susanne Ufermann Fangohr, Thorsten Wittemeier, Ashley Setter, Kieran Selvon, Hossam Ragheb, Craig Rafter, Alvaro Perez-Diaz, Ryan Pepper, David Lusher, Stephen Gow, James Harrison, Paul Chambers, Jan Kamenik, Ioannis Begleris, Robert Entwistle, Jonathon Waters, Rory Brown, Joshua Greenhalgh, Emanuele Zappia
The £10million Centre for Doctoral Training was launched in November 2013 and is jointly funded by EPSRC, the University of Southampton, and its partners.
The NGCM brings together world-class simulation modelling research activities from across the University of Southampton and hosts a 4-year doctoral training programme that is the first of its kind in the UK.
Challenging Topological Prejudice - Automated Airframe Layout Design
Andras Sobester (Investigator), Paul Chambers
Aircraft preliminary design scopes are drastically narrowed by topological prejudice. Modern aircraft have settled on the same 'tube plus wing and cruciform tail' type topology that has been adopted through their ancestry, with no scientific evidence that this layout is optimal. This research project poses the question:
“Given a topologically flexible aircraft geometry that is free of prejudice or bias, would a sophisticated multi-disciplinary optimization process yield a conventional layout?”

Chaotic Analysis of Partial Discharge
Paul Lewin (Investigator), Lyuboslav Petrov
The deterministic character of PD pulses predicted by theory has been shown to be existent for certain PD events. Finding characteristic patterns in phase space enables field-data PD detection with high reliability.

Colonising Polynesia; Uncertain sailing craft route modelling
Thomas Dickson (Investigator), David Sear
Through developing a novel methodology of modelling sailing craft routing it is possible to investigate archaeological problems as well as applications to modern yacht racing and autonomous sailing technology. This research uses iridis to provide accurate and fast analysis of shortest path routes for sailing craft in order to provide insight and improve safety of operation.

Controlling Ant-Based Construction
Seth Bullock (Investigator), Lenka Pitonakova
This paper investigates dynamics of ant nest building and shows that algorithms capable of generating ant-like structures can also be used to create nests, shapes of which are imposed from outside of the system.

CRISIS – Complexity Research Initiative for Systemic InstabilitieS
Frank McGroarty (Investigator), Bob De Caux
A new approach to modelling and understanding financial system and macroeconomic risk and instability

Developing programming skills with Minecraft and Python
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Alvaro Perez-Diaz
PythonTool is a Minecraft mod created for this project which allows interactive execution of Python scripts which interact with the game in real time. It intends to make teaching programming to children or non-expert users easier and more appealing.

Directing magnetic skyrmion traffic flow with nanoscale patterning.
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Mark Vousden
Skyrmions in magnetic nanostructures may lead to new data storage technologies. Appropriate simulation methodologies are developed and applied.
Is the decline in East African lesser flamingo population a natural concequence of soda ake dynamics?
Seth Bullock
An interdisciplinary approach using palaeoenvironmental data analysis and a modelling is being used investigate the dramatic fluctuations in conditions in the East African Rift Valley soda lakes, and how these changes may be impacting the lesser flamingo population.
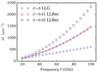
Magnetic dynamics under the Landau-Lifshitz-Baryakhtar equation
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Weiwei Wang
Magnetic dynamics using the Landau-Lifshitz-Baryakhtar (LLBar) equation that the nonlocal damping is included as well as the scalar Gilbert damping.
Magnon-Driven Domain-Wall Dynamics in the presence of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Weiwei Wang
The domain wall motion induced by spin waves (magnons) in the presence of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya Interaction is studied in this project.

Mathematical tools for analysis of genome function, linkage disequilibrium structure and disease gene prediction
Mahesan Niranjan, Andrew Collins, Reuben Pengelly (Investigators)
This iPhD project uses a Gaussian Bayesian Networks framework through Machine learning methods to predict which genes are involved in the development of different diseases.

Mathematical tools for analysis of genome function, linkage disequilibrium structure and disease gene prediction
Mahesan Niranjan, Andrew Collins, Reuben Pengelly (Investigators)
This PhD project uses a Monte Carlo molecular simulation processes approach to predict which genes are involved in the development of different diseases.

Mathematical tools for analysis of genome function, linkage disequilibrium structure and disease gene prediction
Andrew Collins, Mahesan Niranjan, Reuben Pengelly (Investigators), Alejandra Vergara Lope
This iPhD project uses a Gaussian Bayesian Networks approaches framework through machine learning approach to predict which genes are involved in the development of different diseases.
Microstructural modeling of skin mechanics
Georges Limbert (Investigator), Emanuele Zappia
Microstructural modeling of skin mechanics to gain a mechanistic insight into the biomechanics of the skin.
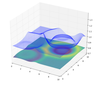
Multiscale modelling of neutron star oceans
Ian Hawke (Investigator), Alice Harpole
Type I X-ray bursts are explosions which occur on the surface of some
neutron stars. It is believed that the burning begins in a localised spot in the ocean of the
star before spreading across the entire surface. By gaining a better understanding of X-ray
bursts, it is hoped that tighter limits can be determined for other neutron star properties
such as the radius and magnetic field strength.
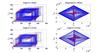
On the applicability of nonlinear timeseries methods for partial discharge analysis
Paul Lewin (Investigator), Lyuboslav Petrov
The governing processes of Partial Discharge (PD)
phenomena trigger aperiodic chains of events resulting in ’ap-
parently’ stochastic data, for which the widely adopted analysis
methodology is of statistical nature. However, it can be shown,
that nonlinear analysis methods can prove more adequate in
detecting certain trends and patterns in complex PD timeseries.
In this work, the application of nonlinear invariants and phase
space methods for PD analysis are discussed and potential pitfalls
are identified. Unsupervised statistical inference techniques based
on the use of surrogate data sets are proposed and employed for
the purpose of testing the applicability of nonlinear algorithms
and methods. The Generalized Hurst Exponent and Lempel Ziv
Complexity are used for finding the location of the system under
test on the spectrum between determinism and stochasticity. The
algorithms are found to have strong classification abilities at
discerning between surrogates and original point series, giving
motivation for further investigations.

OpenDreamKit
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Marijan Beg
OpenDreamKit is a [Horizon 2020](https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/) European Research Infrastructure project (#676541) providing substantial funding to the open-source computational mathematics ecosystem, and in particular popular tools such as LinBox, MPIR, SageMath, GAP, Pari/GP, LMFDB, Singular, MathHub, and the IPython/Jupyter interactive computing environment.
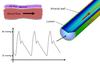
Preventing Alzheimer's Disease: A Multiphysics Simulation Approach
Neil Bressloff, Giles Richardson, Roxana-Octavia Carare (Investigators), Alexandra Diem
Experimental research has identified the causes of many diseases, such as Alzheimer's Disease. However, finding an effective treatment is very cost- and time-intensive and sacrifices many animals and does not guarantee success. In this PhD project, we investigate the driving force of solute drainage in the brain using multiphysics simulations in order to identify possible ways of preventing dementia.
Pushing the Envelope of Planetary Formation and Evolution Simulations
Peter Bartram
A full understanding of the formation and the early evolution of the Solar System and extrasolar planetary systems ranks among natural science's grand challenges, and at present, even the dominant processes responsible for generating the observed planetary architecture remain elusive.
pyQCD
Matthew Spraggs
A basic Python package to perform coarse lattice QCD simulations on desktop and workstation computers.

SAVE: Solent Achieving Value through Efficiency
Patrick James, Ben Anderson (Investigators), Luke Blunden
Analysis of 15 minute electricity consumption and 10 second instantaneous power data from 4,000+ households in the Solent region collected over 3 years of a randomised control trial study.
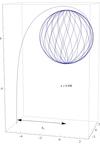
Self-Force and Black Hole Inspirals
Sam Dolan (Investigator)
We use IRIDIS to compute the self-force acting on a solar-mass black hole orbiting a supermassive black hole.
Skyrmionic states in confined nanostructures
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Marijan Beg
An ever increasing need for data storage creates great challenges for the development of high-capacity storage devices that are cheap, fast, reliable, and robust. Because of the fundamental constraints of today's technologies, further progress requires radically different approaches. Magnetic skyrmions are very promising candidates for the development of future low-power, high-capacity, non-volatile data storage devices.
Software Sustainability Institute
Simon Hettrick (Investigator)
A national facility for cultivating world-class research through software
Software helps researchers to enhance their research, and improve the speed and accuracy of their results. The Software Sustainability Institute can help you introduce software into your research or improve the software you already use.
The Institute is based at the universities of Edinburgh, Manchester, Oxford and Southampton, and draws on a team of experts with a breadth of experience in software development, project and programme management, research facilitation, publicity and community engagement.
We help people build better software, and we work with researchers, developers, funders and infrastructure providers to identify key issues and best practice in scientific software.
Spatial variability of the atmosphere in southern England
Joanna Nield, Jason Noble, Edward Milton (Investigators), Robin Wilson
No-one really knows how variable key atmospheric parameters such as Aerosol Optical Thickness and Water Vapour content are over relatively small areas. This study aims to find out!
Studying microevolution in clinical isolates of Neisseria lactamica
Robert Read (Investigator), Jay Laver, Anish Pandey
We intranasally infected and successfully colonised six volunteers with Neisseria lactamica, a commensal species genetically similar to Neisseria meningitidis. A bioinformatics approach was then used to understand the microevolution of this bacterium and its adaptations to the nasopharynx.

Supernova Rates in the Local Universe
Mark Sullivan (Investigator), Christopher Frohmaier
This project will calculate the frequency of exploding stars -- or supernovae -- in the nearby universe. We simulate a 'toy universe' by exploding billions of stars in a computer, and then artificially 'observing' these explosions by replicating a real astronomical sky survey, the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF). The results of this simulation allows us to discover the rate at which supernovae occur in the local universe each year.

Test and Rest
Hans Fangohr (Investigator), Evander DaCosta, James Graham, Oliver Laslett
Regression and system testing, automatic execution of testing - establishing best practice.
The application of automated pattern metrics to surface moisture influences on modelled dune field development
Robin Wilson, Joanna Nield (Investigators)
Areas of sand dunes (known as dunefields) develop complex patterns over time. These are influenced by both the past and present environmental conditions, including surface moisture, vegetation distribution and human impact. This project develops a method of automated pattern analysis which allow the patterns produced by a large number of sand dune evolution simulations (performed using the DECAL model) to be quantified over time.
The Role of the Biota in the Carpenter Model on Lake Eutrophication
James Dyke (Investigator), Alexandra Diem
The Carpenter model is a useful and simple model to predict the eutrophication of shallow lakes via phosphorus input. This project aimed at resolving the function of the biota, which play a major role in the phosphorus dynamics, but are so far only implicitly modelled, and extending the model to explicitly represent them.

Towards design patterns for robot swarms
Richard Crowder, Seth Bullock (Investigators), Lenka Pitonakova
Swarm robotics is an inter-disciplinary field that seeks to design the behaviour of robots that can cooperate effectively on tasks like search and retrieval, reconnaissance, construction, etc. In this project, we are aiming towards a theoretical understanding of swarm intelligence and the development of design patterns for effective robot swarms.

Understanding the Role of Recruitment in Robot Foraging
Seth Bullock, Richard Crowder (Investigators), Lenka Pitonakova
It is shown that recruitment among foraging robots is useful when resources are hard to find, but that the extra cost associated with such robots is not returned when there are many locations to gather from or simply when the relative gain from using communication is low.

Validation of GPS-derived water vapour estimates
Joanna Nield, Jason Noble, Edward Milton (Investigators), Robin Wilson
Measurements from GPS base stations can be processed to provide estimates of the water vapour content in the atmosphere. These are lots of these base stations across the world and they take measurements very frequently, making them perfect data sources for scientific use. However, we need to understand their accuracy - and this project aims to do this.

Vertical turbulence structures in the benthic boundary layer as related to suspended sediments
Hachem Kassem (Investigator), Charlie Thompson
There is a genuine need for better, more robust modelling of suspended sediment transport in the coastal zone, both to understand its morphological evolution and it's impact on biogeochemical cycling, ecosystems services and to guide engineering applications such as dredging and defence schemes against erosion and flooding.
The suspension of sediment in turbulent flows is a complex case of fluid-particle interaction, governed by shear stresses (momentum exchanges) at the bed and within the benthic boundary layer (BBL). The intermittent transfer of momentum is a manifestation of coherent turbulent vortex structures within the flow. The passage of such structures (or clusters of) is often related to perturbations of bottom sediment, which may be entrained and maintained in suspension if sufficient turbulent energy is provided. The first part of my PhD investigated the temporal and scale relationships between wave–generated boundary layer turbulence and event–driven sediment transport in oscillatory flow in the nearshore. This involved complex statistical, spectral, quadrant and wavelet analysis of high frequency nearshore measurements of turbulence and suspended sediments (medium sand), collected as part of the EU-funded Barrier Dynamics Experiment II (BARDEX II). The following step aims to develop a 3D numerical model in OpenFOAM which would reproduce the fine scale turbulence structures observed over a fixed rippled bed in oscillatory flow. The 3D velocity field, turbulent components, correlations (stresses) and quadrant structures will then be linked to observed sediment resuspension events. The model will be validated against a set of laboratory experiments undertaken at the Fast Flow Facility at HR Wallingford.
Whisky Code
Ian Hawke (Investigator)
A 3D finite volume code for simulating compact relativistic hydrodynamics.
People
 Neil Bressloff
Neil BressloffProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Seth Bullock
Seth BullockProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Graeme Day
Graeme DayProfessor, Chemistry (FNES)
 Hans Fangohr
Hans FangohrProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jonathan Flynn
Jonathan FlynnProfessor, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Paul Lewin
Paul LewinProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Frank McGroarty
Frank McGroartyProfessor, Management (FBL)
 Edward Milton
Edward MiltonProfessor, Geography (FSHS)
 Mahesan Niranjan
Mahesan NiranjanProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Mark Nixon
Mark NixonProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Robert Read
Robert ReadProfessor, Medicine (FM)
 Nicolas Green
Nicolas GreenReader, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Peter Horak
Peter HorakReader, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Giles Richardson
Giles RichardsonReader, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Roxana-Octavia Carare
Roxana-Octavia CarareSenior Lecturer, Medicine (FM)
 John Carter
John CarterSenior Lecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Richard Crowder
Richard CrowderSenior Lecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Patrick James
Patrick JamesSenior Lecturer, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Reuben Pengelly
Reuben PengellySenior Lecturer, Medicine (FM)
 James Dyke
James DykeLecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Ian Hawke
Ian HawkeLecturer, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Dina Shona Laila
Dina Shona LailaLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Georges Limbert
Georges LimbertLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Chris-Kriton Skylaris
Chris-Kriton SkylarisLecturer, Chemistry (FNES)
 Andras Sobester
Andras SobesterLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Mark Sullivan
Mark SullivanPrincipal Research Fellow, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Ben Anderson
Ben AndersonSenior Research Fellow, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Jay Laver
Jay LaverSenior Research Fellow, Medicine (FM)
 Charlie Thompson
Charlie ThompsonSenior Research Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Felipe Alves Portela
Felipe Alves PortelaResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alistair Bailey
Alistair BaileyResearch Fellow, Medicine (FM)
 Luke Blunden
Luke BlundenResearch Fellow, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Dirk Broemmel
Dirk BroemmelResearch Fellow, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Sam Dolan
Sam DolanResearch Fellow, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Jacek Dziedzic
Jacek DziedzicResearch Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Patrick Fritzsch
Patrick FritzschResearch Fellow, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Mathis Hain
Mathis HainResearch Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Jason Hilton
Jason HiltonResearch Fellow, Social Sciences (FSHS)
 Hachem Kassem
Hachem KassemResearch Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Thomas Kluyver
Thomas KluyverResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jason Noble
Jason NobleResearch Fellow, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Robin Wilson
Robin WilsonResearch Fellow, Geography (FSHS)
 - -
- -Postgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 David Arden
David ArdenPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Peter Bartram
Peter BartramPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 Ioannis Begleris
Ioannis BeglerisPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Gabriele Boschetto
Gabriele BoschettoPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Rory Brown
Rory BrownPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Paul Chambers
Paul ChambersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Peter Cherry
Peter CherryPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Evander DaCosta
Evander DaCostaPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Bob De Caux
Bob De CauxPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Alexandra Diem
Alexandra DiemPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Samuel Diserens
Samuel DiserensPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Joseph Egan
Joseph EganPostgraduate Research Student, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Anastasia Eleftheriou
Anastasia EleftheriouPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Robert Entwistle
Robert EntwistlePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Christopher Frohmaier
Christopher FrohmaierPostgraduate Research Student, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Stephen Gow
Stephen GowPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Graham
James GrahamPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Joshua Greenhalgh
Joshua GreenhalghPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Harrison
James HarrisonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Garvin Haslett
Garvin HaslettPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Quintin Hill
Quintin HillPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Oliver Laslett
Oliver LaslettPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 David Lusher
David LusherPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Sam Mangham
Sam ManghamPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Vincent Marmion
Vincent MarmionPostgraduate Research Student, Psychology (FSHS)
 Juraj Mihalik
Juraj MihalikPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Walton P. Coutinho
Walton P. CoutinhoPostgraduate Research Student, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Anish Pandey
Anish PandeyPostgraduate Research Student, Medicine (FM)
 Alvaro Perez-Diaz
Alvaro Perez-DiazPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Lyuboslav Petrov
Lyuboslav PetrovPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Lenka Pitonakova
Lenka PitonakovaPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 Daniel Powell
Daniel PowellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Craig Rafter
Craig RafterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Hossam Ragheb
Hossam RaghebPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Álvaro Ruiz-Serrano
Álvaro Ruiz-SerranoPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Ben Samways
Ben SamwaysPostgraduate Research Student, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Kieran Selvon
Kieran SelvonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ashley Setter
Ashley SetterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Maike Sonnewald
Maike SonnewaldPostgraduate Research Student, National Oceanography Centre (FNES)
 Matthew Spraggs
Matthew SpraggsPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Johannes Van Der Horst
Johannes Van Der HorstPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Alejandra Vergara Lope
Alejandra Vergara LopePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jonathon Waters
Jonathon WatersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Iain Weaver
Iain WeaverPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Thorsten Wittemeier
Thorsten WittemeierPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alex Wright
Alex WrightPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Emanuele Zappia
Emanuele ZappiaPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Elisabeth zu-Erbach-Schoenberg
Elisabeth zu-Erbach-SchoenbergPostgraduate Research Student, Management (FBL)
 Matthew Higgins
Matthew HigginsUndergraduate Research Student, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Jess Jones
Jess JonesTechnical Staff, iSolutions
 Petrina Butler
Petrina ButlerAdministrative Staff, Research and Innovation Services
 Susanne Ufermann Fangohr
Susanne Ufermann FangohrAdministrative Staff, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Jan Kamenik
Jan KamenikAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Arthur Lugtigheid
Arthur LugtigheidAlumnus, Psychology (FSHS)
 Nicolas Palopoli
Nicolas PalopoliAlumnus, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Weiwei Wang
Weiwei WangAlumnus, Ningbo University
 Marijan Beg
Marijan BegExternal Member, Imperial College London
 Mark Vousden
Mark VousdenExternal Member, University of Southampton
 Thomas Dickson
Thomas DicksonNone, None
 Simon Hettrick
Simon HettrickNone, None
 Daniel Martinho-Corbishley
Daniel Martinho-CorbishleyNone, None
 David Sear
David SearNone, None