Computer Science

Computer Science covers a wide range of research in addition to Software Engineering, Programming and Scientific Computation.
This topic tag is intended to be used for seminars that are too generic to be described by more specific tags, but fall into the Computer Science remit.
For queries about this topic, contact Hans Fangohr.
View the calendar of events relating to this topic.
Projects
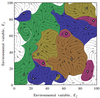
A novel approach to analysing fixed points in complex systems
James Dyke (Investigator), Iain Weaver
This work aims to contribute to our understanding of the relationship between complexity and stability. By describing an abstract coupled life-environment model, we are able to employ novel analytical, and computational techniques to shed light on the properties of such a system.

An Investigation into the Cascade Effect of Mergers on the Global Financial Markets
Seth Bullock, Antonella Ianni (Investigators), Camillia Zedan
An investigation into the external effects that horizontal mergers have on the interconnected global markets.

Automated Algorithmic Trading with Intelligent Execution
Frank McGroarty, Enrico Gerding (Investigators), Ash Booth
In this project, we introduce the first fully automated trading system for real-world stock trading that uses time-adaptive execution algorithm to minimise market impact while increasing profitability com- pared to benchmark strategies.
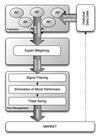
Automated Trading with Performance Weighted Random Forests and Seasonality
Frank McGroarty, Enrico Gerding (Investigators), Ash Booth
This project proposes an expert system that uses novel machine learning techniques to predict the price return over these seasonal events, and then uses these predictions to develop a profitable trading strategy.
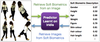
Automatic Image Retrieval with Soft Biometrics for Surveillance
Mark Nixon, John Carter (Investigators), Daniel Martinho-Corbishley
We're investigating ways to automatically describe and identify pedestrians from surveillance footage using human understandable, soft biometric labels. Our goal is to enable surveillance operators to search for pedestrians in a video network using soft biometric descriptions, and to automatically retrieve these descriptions from CCTV images.
Bioclimatic Architecture
Seth Bullock (Investigator), Nicholas Hill
This was a review report on bioclimatic architecture and how such architecture may be designed by agent-based models inspired by the building behaviour of insects.

Can the principle of Maximum Entropy Production be used to predict the steady states of a Rayleigh-Bernard convective system?
Kevin Oliver, Iain Weaver, James Dyke (Investigators)
The principle of Maximum Entropy Production (MEP) has been successfully used to reproduce the steady states of a range of non-equilibrium systems. Here we investigate MEP and maximum heat flux extremum principles directly via the simulation of a Rayleigh-Bérnard convective system implemented as a lattice gas model.

Centre for Doctoral Training in Next Generation Computational Modelling
Hans Fangohr, Ian Hawke, Peter Horak (Investigators), Susanne Ufermann Fangohr, Thorsten Wittemeier, Ashley Setter, Kieran Selvon, Hossam Ragheb, Craig Rafter, Alvaro Perez-Diaz, Ryan Pepper, David Lusher, Stephen Gow, James Harrison, Paul Chambers, Jan Kamenik, Ioannis Begleris, Robert Entwistle, Jonathon Waters, Rory Brown, Joshua Greenhalgh, Emanuele Zappia
The £10million Centre for Doctoral Training was launched in November 2013 and is jointly funded by EPSRC, the University of Southampton, and its partners.
The NGCM brings together world-class simulation modelling research activities from across the University of Southampton and hosts a 4-year doctoral training programme that is the first of its kind in the UK.

Controlling Ant-Based Construction
Seth Bullock (Investigator), Lenka Pitonakova
This paper investigates dynamics of ant nest building and shows that algorithms capable of generating ant-like structures can also be used to create nests, shapes of which are imposed from outside of the system.
Deep Optimisation
Jamie Caldwell
The project will develop the implementation and application of a new optimisation technique. 'Deep optimisation' combines deep learning techniques in neural networks with distributed optimisation methods to create a dynamically re-scalable optimisation process. This project will develop this technique to better-understand its capabilities and limitations and develop GPU implementations. The protein structure prediction problem will be used as the main test application.
Development of wide-ranging functionality in ONETEP
Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigator), Jacek Dziedzic
ONETEP is at the cutting edge of developments in first principles calculations. However, while the fundamental difficulties of performing accurate first-principles calculations with linear-scaling cost have been solved, only a small core of functionality is currently available in ONETEP which prevents its wide application. In this collaborative project between three Universities, the original developers of ONETEP will lead an ambitious workplan whereby the functionality of the code will be rapidly and significantly enriched.
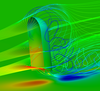
Fluid Structure Interactions of Yacht Sails
Stephen Turnock (Investigator), Daniele Trimarchi
The research is the main subject of the PhD topic. It regards the application of fluid structure interaction techniques to the domain of yacht sails simulation
Generic Operational Simulation of Civil Unmanned Air Vehicle Operations
Hans Fangohr, James Scanlan (Investigators)
This project creates a generic operational simulation of Unmanned Air Vehicle Operations. UAVs can be valued for their mission-suitability and compared against various configurations.

Integrating Automated Vehicles into the Transport Network
Bani Anvari, Ben Waterson (Investigators), Craig Rafter
Innovative new designs to transportation infrastructure - with a strong evidence base - that will support automated vehicles to maximize sustainability in the transport network.
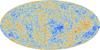
Lattice Holographic Cosmology
Andreas Juttner (Investigator), Matthew Mostert
This project will aim to develop new theoretical field methods and massively parallel computational algorithms to be utilised on both new computational architectures (e.g. Intel Xeon Phi) and existing high performance computers (HPCs).
The ultimate goal is to make predictions for the power spectrum and non-gaussianties of the CMB which would then be falsifiable by comparison to the Planck and WMAP data.
Network Analysis of Roman Transport Routes in the Imperial Roman Mediterranean
David Potts
This research is designed to explore the nature of the relationships between Portus, Rome, and other selected ports in the Mediterranean and to establish patterns and the changing nature of trading networks derived from the distribution of known Roman artefacts.

New Forest Cicada Project
Alexander Rogers, Geoff Merrett (Investigators), Davide Zilli, Oliver Parson
Rediscover the critically endangered New Forest cicada with crowdsourced smartphone biodiversity monitoring techniques.
Nonequilibrium Dynamics of Atomic Gases in Optical Lattices
Sophie Marika Reed
Many-body, quantum systems exhibit emergent properties which allows for quantum events to influence properties on macroscopic scales. Such emergent properties are studied using stochastic phase-space techniques.
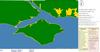
Operational Simulation of the Solent Search-and-Rescue environment
James Scanlan, Kenji Takeda, Hans Fangohr (Investigators), Ben Schumann
This project aims to identify useful metrics for a proposed Search-and-Rescue UAV and test it virtually in a realistic environment.

Origins of Evolvability
Richard Watson, Markus Brede (Investigators), William Hurndall
This project examined the putative evolvability of a Lipid World model of fissioning micelles. It was demonstrated that the model lacked evlovability due to poor heritability. Explicit structure for micelles was introduced along with a spatially localised form of catalysis which increased the strength of selection as coupling between potential chemical units of heredity were reduced.

Predicting Available Energy in Energy Harvesting Wireless Sensor Networks
Geoff Merrett (Investigator), Davide Zilli
Is it possible to predict how much energy a sun-light or wind powered wireless sensor node can harvest and tune its sensing pattern accordingly?
Pushing the Envelope of Planetary Formation and Evolution Simulations
Peter Bartram
A full understanding of the formation and the early evolution of the Solar System and extrasolar planetary systems ranks among natural science's grand challenges, and at present, even the dominant processes responsible for generating the observed planetary architecture remain elusive.
Quantifying Collective Construction
Seth Bullock (Investigator), Nicholas Hill
This was an initial investigation into how best to develop quantifying and discriminating measures of both the processes and results of collective construction.
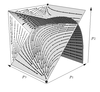
Renormalisation group approach to 1D cellular automata with large updating neighbourhoods
Iain Weaver, Adam Prugel-Bennett (Investigators)
We study self-similarity in one-dimensional probabilistic cellular automata (PCA) by applying a real-space renormalisation technique to PCA with increasingly large updating neighbourhoods. By studying the flow about the critical point of the renormalisation, we may produce estimates of the spatial scaling properties of critical PCA.
Renormalisation of 2D cellular automata with an absorbing state
Adam Prugel-Bennett, Iain Weaver (Investigators)
We describe a real-space renormalisation scheme for non-equilibrium probablistic cellular automata (PCA) models, and apply it to a two-dimensional binary PCA. An exact renormalisation scheme is rare, and therefore we provide a method for computing the stationary probability distribution of states for such models with which to weight the renormalisation, effectively minimising the error in the scale transformation.
Sensitivity of the critical depth to the choice of particle movement rules in Lagrangian models and the consequences for the predicted timing of the spring bloom
Tom Anderson (Investigator), Melissa Saeland
Individual-based (Lagrangian) models lend themselves to the study of the controls of the spring bloom in the ocean, due to their ability to represent both the turbulence and the phytoplankton motion. Here, we use a Lagrangian phytoplankton model to test some of the most prevalent hypotheses (e.g. critical depth and critical turbulence).
Software Sustainability Institute
Simon Hettrick (Investigator)
A national facility for cultivating world-class research through software
Software helps researchers to enhance their research, and improve the speed and accuracy of their results. The Software Sustainability Institute can help you introduce software into your research or improve the software you already use.
The Institute is based at the universities of Edinburgh, Manchester, Oxford and Southampton, and draws on a team of experts with a breadth of experience in software development, project and programme management, research facilitation, publicity and community engagement.
We help people build better software, and we work with researchers, developers, funders and infrastructure providers to identify key issues and best practice in scientific software.
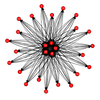
Spatial Mobility in the Formation of Agent-Based Economic Networks
Antonella Ianni, Seth Bullock (Investigators), Camillia Zedan
An investigation into the effect of spatial mobility on endogenous economic network formation.
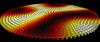
Stability of chiral structures in magnetic nanodisks
Hans Fangohr, Weiwei Wang (Investigators), David Cortes
This project is aimed to study the stability of skyrmionic and helical equilibrium states in magnetic nanodisks, using computational simulations.
Sustainable domain-specific software generation tools for extremely parallel particle-based simulations
Chris-Kriton Skylaris (Investigator)
A range of particle based methods (PBM) are currently used to simulate materials in chemistry, engineering, physics and biophysics. The 4 types of PBM considered directly in the proposed are molecular dynamics (MD), the ONETEP quantum mechanics-based program, discrete element modelling (DEM), and smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH).
The overall research objective is to develop a sustainable tool that will deliver, in the future, cutting edge research applicable to applications ranging from dam engineering to atomistic drug design.

Testing an interaction game on relationships.
Seth Bullock (Investigator), Anastasia Eleftheriou
The aim of this project is to examine how attractiveness is related to hypothetical risky sexual behaviour. The term `risky sexual behaviour' refers to having multiple sexual partners without the use of a condom. Data will be collected using questionnaires in order to investigate the influence of attractiveness on intentions towards engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse. A primary research question is whether perceived attractiveness of a potential partner affects the reported likelihood of having sex and/or using a condom.

The Endogenous Formation of Economic Networks
Antonella Ianni, Seth Bullock (Investigators), Camillia Zedan
An investigation into endogenous network formation using a simple agent-based approach.
The importance of timescales for the emergence of environmental self-regulation
Iain Weaver, James Dyke (Investigators)
Models which explore the possibilities of emergent self-regulation in the Earth system often assume the timescales associated with changes in various sub-systems to be predetermined. We analyse a classic model of environmental self-regulation, Daisyworld, and interpret the original equations for model temperature, changes in insolation, and self-organisation of the biota as an important separation of timescales.

THE NORM MATE TRANSPORTER FROM N. GONORRHEAE: INSIGHTS INTO DRUG & ION BINDING FROM ATOMISTIC MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS
Syma Khalid (Investigator), Daniel Holdbrook, Thomas Piggot, Yuk Leung
The multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) transporters extrude a wide variety of substrates out of both mammalian and bacterial cells via the electrochemical gradient of protons and cations across the membrane. Multiple atomistic simulation are performed on a MATE transporter, NorM from Neisseria gonorrheae (NorM_NG) and NorM from Vibrio cholera (NorM_VC). These simulations have allowed us to identify the nature of the drug-protein/ion-protein interactions, and secondly determine how these interactions contribute to the conformational rearrangements of the protein.

The Perks of Complexity Reduction
Lajos Hanzo (Investigator), Chao Xu
Reliable high-speed modems facilitate ubiquitous communications in our daily lives amongst people and/or machines. The communication technologies we need for the future have to have a high reliability and a low cost. My research aims for reducing the complexity of state-of-the-art communication systems, so that they can communicate in real time at an increased throughput. Naturally having access to parallel computers such as Iridis gives my research a competitive advantage over other researchers, relying on slower simulations.

The Role of Information in Price Discovery
Antonella Ianni, Seth Bullock (Investigators), Camillia Zedan
The recent economic crisis has highlighted a continued vulnerability and lack of understanding in the financial markets. In order to overcome this, many believe that current market models must be improved. Recently, a trend towards agent-based modelling has emerged. Viewing the economy as a complex system is beginning to be seen as key to explaining certain market characteristics that were originally considered anomalies.
One of the fundamental assumptions in economics is that of information efficiency: that the price of a stock reflects its worth, that all possible information about a security is publicly known, and that any changes to price take place instantaneously. In reality, however, this is not the case.
This project considers the use of agents in modelling economic systems and demonstrates the effect of information levels on price discovery using a simple market simulation.

The Social-cognitive Niche: An Exploration of the Co-evolutionary Relationship between Human Mind and language, with a Particular Focus of the Self-organisational properties of the Emergence of Symbolic Representation.
Jason Noble, Glyn Hicks (Investigators), Lewys Brace
This work explored the relationship between the origin and subsequent evolution of the human mind and language; a relationship that is believed to be symbiotic in nature. This piece aimed to achieve two objectives. Firstly, it set out a theoretical framework, using the principles of complexity theory and self-organisation, which attempts to explain this relationship from a holistic perspective.
Secondly, it presented an agent-based model of a vervet monkey social group, which sought to investigate the variables that were perceived to underpin the emergence of symbolic representation within a population of language users.
The belief here was that, by understanding the influence of these variables, one would be able to better understand the genesis of the aforementioned relationship.
Traveling and movement during European Late Prehistory
Patricia Murrieta Flores
This project has as main purpose to investigate through spatial analysis and computational modelling the variables and factors that influenced how humans traveled during prehistoric times.
One of the principal objectives will be to clarify the role that certain landscape elements (i.e megalithic monuments) played in terrestrial navigation and territorial definition.
This project is supported by CONACYT (Mexico) as a doctoral research by Patricia Murrieta-Flores under the supervision of Dr. David Wheatley (University of Southampton) and Dr. Leonardo Garcia Sanjuan (University of Seville, Spain). It also counts with the collaboration of Dr. Dimitrij Mlekuz (Gent University, Belgium).

Understanding the Role of Recruitment in Robot Foraging
Seth Bullock, Richard Crowder (Investigators), Lenka Pitonakova
It is shown that recruitment among foraging robots is useful when resources are hard to find, but that the extra cost associated with such robots is not returned when there are many locations to gather from or simply when the relative gain from using communication is low.
People
 Seth Bullock
Seth BullockProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Hans Fangohr
Hans FangohrProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Lajos Hanzo
Lajos HanzoProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Frank McGroarty
Frank McGroartyProfessor, Management (FBL)
 Mark Nixon
Mark NixonProfessor, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 James Scanlan
James ScanlanProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stephen Turnock
Stephen TurnockProfessor, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Peter Horak
Peter HorakReader, Optoelectronics Research Centre
 Andreas Juttner
Andreas JuttnerReader, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Markus Brede
Markus BredeSenior Lecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 John Carter
John CarterSenior Lecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Richard Crowder
Richard CrowderSenior Lecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Antonella Ianni
Antonella IanniSenior Lecturer, Social Sciences (FSHS)
 Richard Watson
Richard WatsonSenior Lecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Bani Anvari
Bani AnvariLecturer, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Dyke
James DykeLecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Ian Hawke
Ian HawkeLecturer, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Glyn Hicks
Glyn HicksLecturer, Humanities (FH)
 Geoff Merrett
Geoff MerrettLecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Kevin Oliver
Kevin OliverLecturer, National Oceanography Centre (FNES)
 Alexander Rogers
Alexander RogersLecturer, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Chris-Kriton Skylaris
Chris-Kriton SkylarisLecturer, Chemistry (FNES)
 Ben Waterson
Ben WatersonLecturer, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Tom Anderson
Tom AndersonPrincipal Research Fellow, National Oceanography Centre (FNES)
 Syma Khalid
Syma KhalidPrincipal Research Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Richard Boardman
Richard BoardmanSenior Research Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Felipe Alves Portela
Felipe Alves PortelaResearch Fellow, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Petros Bogiatzis
Petros BogiatzisResearch Fellow, Ocean & Earth Science (FNES)
 Taihai Chen
Taihai ChenResearch Fellow, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jacek Dziedzic
Jacek DziedzicResearch Fellow, Chemistry (FNES)
 Btissam Er-Rahmadi
Btissam Er-RahmadiResearch Fellow, Management (FBL)
 Jason Noble
Jason NobleResearch Fellow, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Joseph Abram
Joseph AbramPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Roxana Aldea
Roxana AldeaPostgraduate Research Student, Mathematics (FSHS)
 David Arden
David ArdenPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jordi Arranz
Jordi ArranzPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Peter Bartram
Peter BartramPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 Patrick Bechlars
Patrick BechlarsPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ioannis Begleris
Ioannis BeglerisPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Harry Beviss
Harry BevissPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Ash Booth
Ash BoothPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Lewys Brace
Lewys BracePostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Rory Brown
Rory BrownPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Jamie Caldwell
Jamie CaldwellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Paul Chambers
Paul ChambersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Dmitri Chernyshenko
Dmitri ChernyshenkoPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 David Cortes
David CortesPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Alicia Costalago Meruelo
Alicia Costalago MerueloPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 Paul Cross
Paul CrossPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Evander DaCosta
Evander DaCostaPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Caroline Duignan
Caroline DuignanPostgraduate Research Student, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Anastasia Eleftheriou
Anastasia EleftheriouPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Graham Elliott
Graham ElliottPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Robert Entwistle
Robert EntwistlePostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Darius Pepe Falahat
Darius Pepe FalahatPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Stephen Gow
Stephen GowPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Joshua Greenhalgh
Joshua GreenhalghPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 James Harrison
James HarrisonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Garvin Haslett
Garvin HaslettPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Nicholas Hill
Nicholas HillPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 William Hurndall
William HurndallPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Adam Jackson
Adam JacksonPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Leo Jofeh
Leo JofehPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Andrew Lawson
Andrew LawsonPostgraduate Research Student, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 Yuk Leung
Yuk LeungPostgraduate Research Student, Chemistry (FNES)
 Edwin Lizarazo
Edwin LizarazoPostgraduate Research Student, Physics & Astronomy (FPAS)
 David Lusher
David LusherPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Vincent Marmion
Vincent MarmionPostgraduate Research Student, Psychology (FSHS)
 Matthew Mostert
Matthew MostertPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Patricia Murrieta Flores
Patricia Murrieta FloresPostgraduate Research Student, Humanities (FH)
 Gregory Parkes
Gregory ParkesPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Alvaro Perez-Diaz
Alvaro Perez-DiazPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Lyuboslav Petrov
Lyuboslav PetrovPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Lenka Pitonakova
Lenka PitonakovaPostgraduate Research Student, University of Southampton
 David Potts
David PottsPostgraduate Research Student, Humanities (FH)
 Daniel Powell
Daniel PowellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Stephen Powell
Stephen PowellPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Craig Rafter
Craig RafterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Hossam Ragheb
Hossam RaghebPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Sophie Marika Reed
Sophie Marika ReedPostgraduate Research Student, Mathematics (FSHS)
 Melissa Saeland
Melissa SaelandPostgraduate Research Student, National Oceanography Centre (FNES)
 Ben Schumann
Ben SchumannPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Kieran Selvon
Kieran SelvonPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Ashley Setter
Ashley SetterPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Nathan Smith
Nathan SmithPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 James Snowdon
James SnowdonPostgraduate Research Student, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Nick Synes
Nick SynesPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Daniele Trimarchi
Daniele TrimarchiPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Johannes Van Der Horst
Johannes Van Der HorstPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Valerio Vitale
Valerio VitalePostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Jonathon Waters
Jonathon WatersPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Iain Weaver
Iain WeaverPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Thorsten Wittemeier
Thorsten WittemeierPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Chao Xu
Chao XuPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Emanuele Zappia
Emanuele ZappiaPostgraduate Research Student, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Camillia Zedan
Camillia ZedanPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Davide Zilli
Davide ZilliPostgraduate Research Student, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Matthew Higgins
Matthew HigginsUndergraduate Research Student, Biological Sciences (FNES)
 Jess Jones
Jess JonesTechnical Staff, iSolutions
 Elena Vataga
Elena VatagaTechnical Staff, iSolutions
 Petrina Butler
Petrina ButlerAdministrative Staff, Research and Innovation Services
 Susanne Ufermann Fangohr
Susanne Ufermann FangohrAdministrative Staff, Civil Engineering & the Environment (FEE)
 Ella Marley-Zagar
Ella Marley-ZagarEnterprise staff, Medicine (FM)
 Erika Quaranta
Erika QuarantaEnterprise staff, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Jan Kamenik
Jan KamenikAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Dan Mason
Dan MasonAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Mohsen Mesgarpour
Mohsen MesgarpourAlumnus, University of Southampton
 Oliver Parson
Oliver ParsonAlumnus, Electronics and Computer Science (FPAS)
 Kenji Takeda
Kenji TakedaAlumnus, Engineering Sciences (FEE)
 Weiwei Wang
Weiwei WangAlumnus, Ningbo University
 Marijan Beg
Marijan BegExternal Member, Imperial College London
 Daniel Pope
Daniel PopeExternal Member, Mauve Internet Ltd.
 Mark Vousden
Mark VousdenExternal Member, University of Southampton
 Enrico Gerding
Enrico GerdingNone, None
 Simon Hettrick
Simon HettrickNone, None
 Daniel Holdbrook
Daniel HoldbrookNone, None
 Daniel Martinho-Corbishley
Daniel Martinho-CorbishleyNone, None
 Thomas Piggot
Thomas PiggotNone, None
 Daisuke Sasaki
Daisuke SasakiNone, None
 Sheng Yang
Sheng YangNone, None